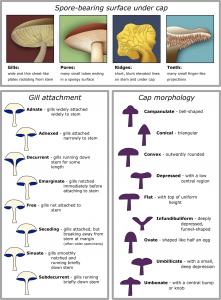
A mushroom is the meaty, spore-bearing fruiting assembly of a parasite, normally generated over the ground on soil or on its sustenance root. The standard for the name “mushroom” is the developed white catch mushroom, Agaricus bisporus; henceforth the saying “mushroom” is most frequently had an association with those organisms (Basidiomycota, Agaricomycetes) that have a stem (stipe), a top (pileus), and gills (lamellae, sing. lamella) or pores on the underside of the top.
Related posts:
Humans & Animals
Anthrozoology (in addition called human–animal studies or HAS) is the investigation of connection between living things. It's a current interdisciplinary and burgeoning field that covers with various different restrains, incorporating human studies, ethology, drug, psychology, veterinary drug and zoology. A major center of anthrozoologic research is the quantifying of the positive impacts of human...
Anthrozoology (in addition called human–animal studies or HAS) is the investigation of connection between living things. It's a current interdisciplinary and burgeoning field that covers with various different restrains, incorporating human studies, ethology, drug, psychology, veterinary drug and zoology. A major center of anthrozoologic research is the quantifying of the positive impacts of human...
Brain Dominance
The Herrmann Mind Strength Instrument is a system ensured to measure and depict thinking slant in people, enhanced by William "Ned" Herrmann while propelling government direction at General Electric's Crotonville office. It is a sort of cognitive style estimation and model tantamount to the Myers-Briggs Sort Marker, Picking up Introduction Survey, DISC examination, and others.
The Herrmann Mind Strength Instrument is a system ensured to measure and depict thinking slant in people, enhanced by William "Ned" Herrmann while propelling government direction at General Electric's Crotonville office. It is a sort of cognitive style estimation and model tantamount to the Myers-Briggs Sort Marker, Picking up Introduction Survey, DISC examination, and others.
Respiratory Sytem
The respiratory system (or ventilatory framework) is the biotic framework of a creature that acquaints respiratory gases with the inner part and performs gas trade. In people and different vertebrates, the anatomical emphasizes of the respiratory framework incorporate aviation routes, lungs, and the respiratory muscles. Atoms of oxygen and carbon dioxide are inactively traded, by dissemination, be...
The respiratory system (or ventilatory framework) is the biotic framework of a creature that acquaints respiratory gases with the inner part and performs gas trade. In people and different vertebrates, the anatomical emphasizes of the respiratory framework incorporate aviation routes, lungs, and the respiratory muscles. Atoms of oxygen and carbon dioxide are inactively traded, by dissemination, be...
Human Evolution
Human development points to the evolutionary process hinting at the manifestation of cutting edge people. While it started with the final regular progenitor of all essence, the subject ordinarily just blankets the evolutionary history of primates, specifically the class Homo, and the development of Homo sapiens as a dissimilar animal category of primates (or "foremost chimps"). The investigation o...
Human development points to the evolutionary process hinting at the manifestation of cutting edge people. While it started with the final regular progenitor of all essence, the subject ordinarily just blankets the evolutionary history of primates, specifically the class Homo, and the development of Homo sapiens as a dissimilar animal category of primates (or "foremost chimps"). The investigation o...
Sleep
Sleep is a typically repeating state portrayed by decreased or truant awareness, comparatively suspended tactile action, and inertia of practically all voluntary muscles. It's recognized from calm wakefulness by a diminished capacity to respond to stimuli, and is more effectively reversible than being in hibernation or a trance like state. Rest is an increased anabolic state, highlighting the deve...
Sleep is a typically repeating state portrayed by decreased or truant awareness, comparatively suspended tactile action, and inertia of practically all voluntary muscles. It's recognized from calm wakefulness by a diminished capacity to respond to stimuli, and is more effectively reversible than being in hibernation or a trance like state. Rest is an increased anabolic state, highlighting the deve...
Metabolism
Metabolism is the situated of essence-upholding compound transformations within the cells of living life forms. The proposed chemical-catalyzed responses permit living beings to develop and duplicate, uphold their structures, and react to their surroundings. The expression metabolism can likewise point to all substance responses that happen in living life forms, incorporating assimilation and the ...
Metabolism is the situated of essence-upholding compound transformations within the cells of living life forms. The proposed chemical-catalyzed responses permit living beings to develop and duplicate, uphold their structures, and react to their surroundings. The expression metabolism can likewise point to all substance responses that happen in living life forms, incorporating assimilation and the ...
Swine Flu Stats A
Swine flu, likewise called pig flu, swine influenza, hoard influenza and pig influenza, is a contamination brought about by any of a few sorts of swine flu viruses. Swine flu virus (SIV) or swine-cause flu virus (S-OIV) is any strain of the flu group of viruses that is endemic in pigs. As of 2009, the known SIV strains incorporate flu C and the subtypes of flu A reputed to be H1N1, H1N2, H2N1, H3N...
Swine flu, likewise called pig flu, swine influenza, hoard influenza and pig influenza, is a contamination brought about by any of a few sorts of swine flu viruses. Swine flu virus (SIV) or swine-cause flu virus (S-OIV) is any strain of the flu group of viruses that is endemic in pigs. As of 2009, the known SIV strains incorporate flu C and the subtypes of flu A reputed to be H1N1, H1N2, H2N1, H3N...
Brain Waves
Neural swaying is cadenced or tedious neural movement in the midway apprehensive framework. Neural tissue can create oscillatory action in a significant number of ways, driven either by mechanisms restricted within unique neurons or by connections between neurons. In distinctive neurons, motions can seem either as motions in film potential or as musical designs of movement potentials, which then g...
Neural swaying is cadenced or tedious neural movement in the midway apprehensive framework. Neural tissue can create oscillatory action in a significant number of ways, driven either by mechanisms restricted within unique neurons or by connections between neurons. In distinctive neurons, motions can seem either as motions in film potential or as musical designs of movement potentials, which then g...
Cloning
Cloning in science is the method of transforming comparable inhabitant numbers of hereditarily indistinguishable people that happens in nature when living beings for example microscopic organisms, bugs or plants repeat agamically. Cloning in biotechnology points to methods long ago would make duplicates of DNA parts (sub-atomic cloning), cells (unit cloning), or living beings. The term in addition...
Cloning in science is the method of transforming comparable inhabitant numbers of hereditarily indistinguishable people that happens in nature when living beings for example microscopic organisms, bugs or plants repeat agamically. Cloning in biotechnology points to methods long ago would make duplicates of DNA parts (sub-atomic cloning), cells (unit cloning), or living beings. The term in addition...
Blood Type Compatability
A blood type consists of of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells.
A blood type consists of of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells.
HB Spinal System A
The spinal line is an extended, slight, tubular heap of apprehensive tissue and uphold cells that develops from the cerebrum (the medulla oblongata in particular). The mind and spinal line as one unit make up the midway anxious framework (CNS). The spinal string starts at the occipital bone and grows down to the space between the first and second lumbar vertebrae; it tries not to enlarge the whole...
The spinal line is an extended, slight, tubular heap of apprehensive tissue and uphold cells that develops from the cerebrum (the medulla oblongata in particular). The mind and spinal line as one unit make up the midway anxious framework (CNS). The spinal string starts at the occipital bone and grows down to the space between the first and second lumbar vertebrae; it tries not to enlarge the whole...
Genetic Families
The grouping of nucleotides in a gene is interpreted by units to handle a chain of amino acids, making proteins—the request of amino acids in a protein compares to the request of nucleotides in the gene. This association between nucleotide succession and amino harsh corrosive arrangement is reputed to be the hereditary code. The amino acids in a protein confirm how it overlap into a several-di...
The grouping of nucleotides in a gene is interpreted by units to handle a chain of amino acids, making proteins—the request of amino acids in a protein compares to the request of nucleotides in the gene. This association between nucleotide succession and amino harsh corrosive arrangement is reputed to be the hereditary code. The amino acids in a protein confirm how it overlap into a several-di...
HB Arterial System
Arteries are gore vessels that divert crimson ooze from the heart. This crimson ooze is ordinarily oxygenated, exemptions made for the aspiratory and umbilical supply routes. The EABV is that ICF liquid which fills the blood vessel framework.
Arteries are gore vessels that divert crimson ooze from the heart. This crimson ooze is ordinarily oxygenated, exemptions made for the aspiratory and umbilical supply routes. The EABV is that ICF liquid which fills the blood vessel framework.
QS Anatomy II (1)
Anatomy is a limb of diagnosis and prescription that recognizes the structure of living things. It's a general term that incorporates human life structures, creature life structures (zootomy), and plant life systems (phytotomy). In some of its features life systems is nearly identified with embryology, near life systems and relative embryology,through regular establishes in advancement.
Anatomy is a limb of diagnosis and prescription that recognizes the structure of living things. It's a general term that incorporates human life structures, creature life structures (zootomy), and plant life systems (phytotomy). In some of its features life systems is nearly identified with embryology, near life systems and relative embryology,through regular establishes in advancement.
SC Microbiology (3)
Microbiological methodology commonly should be aseptic, and utilize a mixture of devices for example light magnifying instruments with a combo of stains and dyes.The most usually utilized stains are called essential colors, and are made out of absolutely charged particles. Two sorts of fundamental colors are basic stains and differential stains. Effortless stains comprise of one color and distingu...
Microbiological methodology commonly should be aseptic, and utilize a mixture of devices for example light magnifying instruments with a combo of stains and dyes.The most usually utilized stains are called essential colors, and are made out of absolutely charged particles. Two sorts of fundamental colors are basic stains and differential stains. Effortless stains comprise of one color and distingu...
Tree of Life A
The notion of a tree of essence has been utilized within science, religion, reasoning, and mythology. A tree of existence is a normal theme in different globe religious philosophies, mythologies, and theories. An enchanted thought suggesting the interconnection of all essence on our planet; and an analogy for normal plummet in the evolutionary sense. The term tree of existence may additionally be ...
The notion of a tree of essence has been utilized within science, religion, reasoning, and mythology. A tree of existence is a normal theme in different globe religious philosophies, mythologies, and theories. An enchanted thought suggesting the interconnection of all essence on our planet; and an analogy for normal plummet in the evolutionary sense. The term tree of existence may additionally be ...
DNA Facts
Deoxyribonucleic harsh corrosive (DNA) particles are enlightening atoms encoding the hereditary directions utilized within the growth and working of all known living life forms and numerous viruses. On top of RNA and proteins, DNA is one of the several major macromolecules that are key for all known types of essence. Hereditary informative data is encoded as a grouping of nucleotides (guanine, ade...
Deoxyribonucleic harsh corrosive (DNA) particles are enlightening atoms encoding the hereditary directions utilized within the growth and working of all known living life forms and numerous viruses. On top of RNA and proteins, DNA is one of the several major macromolecules that are key for all known types of essence. Hereditary informative data is encoded as a grouping of nucleotides (guanine, ade...
Eye Color Genetics
Complex eyes can recognize shapes and colours. The superficial fields of numerous organic entities, specifically predators, include great ranges of binocular vision to enhance profundity observation. In different living beings, eyes are spotted in order to maximise the field of view, for example in rabbits and stallions, which have monocular vision.
Complex eyes can recognize shapes and colours. The superficial fields of numerous organic entities, specifically predators, include great ranges of binocular vision to enhance profundity observation. In different living beings, eyes are spotted in order to maximise the field of view, for example in rabbits and stallions, which have monocular vision.

 Upload your infographic here and contribute to our community.
Upload your infographic here and contribute to our community. 
Leave a Reply