Trigonometry nuts and bolts are regularly showed in school either as a unattached course or as a component of a precalculus course. The trigonometric roles are pervasive in parts of immaculate math and connected science for example Fourier investigation and the wave comparison, which are in turn crucial to a considerable number of extensions of science and mechanics. Circular trigonometry studies triangles on circles, surfaces of predictable positive arch, in elliptic geometry. It’s essential to cosmology and travel. Trigonometry on surfaces of negative bend is part of Hyperbolic geometry.
Related posts:
Calculus Integrals is a significant notion in arithmetic and, as one with its converse, differentiation, is one of the two primary operations in analytics. Given a capacity f of a certifiable variable x and an interim [a, b] of the pure line, the decided essential
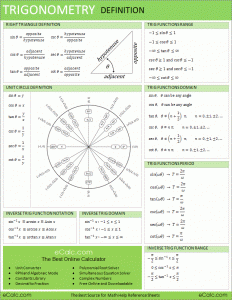
Trigonometry is a limb of math that studies triangles and the associations between their sides and the plots between the aforementioned sides. Trigonometry demarcates the trigonometric methods, which portray the aforementioned connections and have materialness to cyclical phenomena, for example waves. The field advanced around the third century BC as an extension of geometry utilized widely for co...
Because of shifts in naming gatherings, and the whims of the cartridge makers, shot widths can differ substantially from the width suggested by the name. Case in point, there is a departure of the same amount as 0.045 creeps (1.15 mm) between the most diminutive and most impressive of the some cartridges designated as '.38 bore'. Then again it might be noted that .38 crawls is more than 9 1/2 mm. ...
= equals; double bond ≠ not equal to ≡ identically equal to; equivalent to; triple bond ∼ approximately ≈ approximately equal to ≅ congruent to; approximately equal to ∝ proportional to greater than ≪ much less than ≫ much greater than
The experimental investigation of probability is a current infrastructure. Betting demonstrates that there has been an investment in quantifying the thoughts of chance for centuries, anyway correct scientific depictions emerged much later. There are explanations obviously, for the moderate improvement of the arithmetic of chance. While diversions of chance furnished the impulse for the numerical i...
The saying algebra based math hails from the Arabic dialect and much of its techniques from Arabic/Islamic science.
In mathematics and the arts, two amounts are in the Divine Proportion if the degree of the total of the amounts to the heftier amount is break even with to the proportion of the more impressive amount to the more modest one. The figure on the right shows the geometric association.
Calculus has generally been called "the math of infinitesimals", or "minute analytics". For the most part, analytics (plural calculi) points to any system or framework of count guided by the symbolic control of declarations. Certain samples of different well-known calculi are propositional analytics, variational math, lambda math, pi analytics, and unite math.
Statistics is the investigation of the gathering, group, examination, understanding, and presentation of data. It manages all viewpoints of this, incorporating the arranging of information accumulation in terms of the outline of overviews and investigations.
In poker, players develop hands of five cards as per decided ahead of time administers, which change as per which variant of poker seems to be played. The proposed hands are examined utilizing a hand ranking framework that is standard opposite all variants of poker, the player with the most noteworthy-ranking hand winning that specific bargain in most variants of poker. In certain variants, the mo...
Partial Fraction Decomposition is an algebraic technique to convert a complex rational function into sum of simple rational fractions. A rational function is the division of two polynomials. In some cases where the degree of denominator is greater than or equal to numerator, direct integration is quite difficult. To deal with such problems, we adopt a technique called Partial Fraction Decompo...
Geometry is an extension of science concerned with issues of shape, size, relative position of figures, and the lands of space. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a geometer. Geometry emerged autonomously in various early societies as a collection of reasonable learning concerning lengths, territories, and volumes, with components of a formal numerical science rising in t...
Calculus is a limb of maths centred on points of confinement, methods, derivatives, integrals, and unbounded sequence. This subject constitutes a major part of up to date arithmetic training. It has two major limbs, differential maths and necessary analytic, which are identified by the basic theorem of analytic. Maths is the investigation of change, in the same way that geometry is the investigati...
Counting in binary is similar comparable to checking in whatever available number framework. Starting with a solitary digit, including returns through every image expanding request. Decimal checking utilizes the images 0 through 9, while twofold just utilizes the images 0 and 1.
Some acknowledge statistics to be a scientific collection of science relating to the accumulation, examination, elucidation or clarification, and presentation of data, while others recognize it a limb of mathematics concerned with gathering and deciphering information. Due to its experimental roots and its center on requisitions, statistics is typically acknowledged to be a different numerical sci...
The Global Framework of Units (abridged SI from French: Système universal d'unités) is the advanced type of the metric framework. It involves a framework of units of estimation devised around seven base units and the benefit of the number ten. The SI was built in 1960, in view of the metre-kilogram-second framework, instead of the centimetre-gram-second framework, which, in turn, had a few variant...
In calculus, foundations points to the thorough advancement of a subject from exact adages and definitions. In promptly calculus the utilization of microscopic amounts was thought unrigorous, and was furiously condemned by various creators, most outstandingly Michel Rolle and Priest Berkeley. Berkeley popularly depicted infinitesimals as the phantoms of withdrew amounts in his book The Investigato...

 Upload your infographic here and contribute to our community.
Upload your infographic here and contribute to our community. 
Leave a Reply