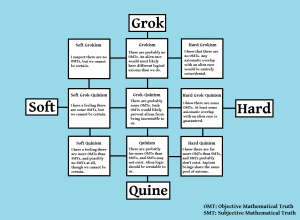
Quine’s position: that goal scientific truths exist, and if there are outsiders they could perceive our math.
Grok’s position: that goal scientific truths don’t exist, and if there are outsiders they could have no idea how to comprehend our math.
Related posts:
SC Calculus I (3)
The formal investigation of calculus consolidated Cavalieri's infinitesimals with the math of limited divergences advanced in Europe at around the same time. Pierre de Fermat, guaranteeing that he acquired from Diophantus, presented the idea of adequality, which acted for fairness up to a minute failure term. The synthesis was attained by John Wallis, Isaac Pushcart, and James Gregory, the last tw...
The formal investigation of calculus consolidated Cavalieri's infinitesimals with the math of limited divergences advanced in Europe at around the same time. Pierre de Fermat, guaranteeing that he acquired from Diophantus, presented the idea of adequality, which acted for fairness up to a minute failure term. The synthesis was attained by John Wallis, Isaac Pushcart, and James Gregory, the last tw...
Maths CS
Trigonometry is a limb of math that studies triangles and the associations between their sides and the plots between the aforementioned sides. Trigonometry demarcates the trigonometric methods, which portray the aforementioned connections and have materialness to cyclical phenomena, for example waves. The field advanced around the third century BC as an extension of geometry utilized widely for co...
Trigonometry is a limb of math that studies triangles and the associations between their sides and the plots between the aforementioned sides. Trigonometry demarcates the trigonometric methods, which portray the aforementioned connections and have materialness to cyclical phenomena, for example waves. The field advanced around the third century BC as an extension of geometry utilized widely for co...
SC Algebra I (3)
The saying algebra based math hails from the Arabic dialect and much of its techniques from Arabic/Islamic science.
The saying algebra based math hails from the Arabic dialect and much of its techniques from Arabic/Islamic science.
Math Tree
In math and statistical strategies, a tree graph is utilized to figure the chance of getting particular consequences where the conceivable outcomes are settled. (See speculative and trial prospect).
In math and statistical strategies, a tree graph is utilized to figure the chance of getting particular consequences where the conceivable outcomes are settled. (See speculative and trial prospect).
Card Counting
Card Counting is a club card event methodology utilized fundamentally within the blackjack group of clubhouse recreations to certify if the subsequently hand is possible to give a feasible playing point to the player or to the dealer. Card counters, moreover reputed further bolstering be good fortune players, endeavor to reduction the intrinsic clubhouse house edge by keeping a running tally of al...
Card Counting is a club card event methodology utilized fundamentally within the blackjack group of clubhouse recreations to certify if the subsequently hand is possible to give a feasible playing point to the player or to the dealer. Card counters, moreover reputed further bolstering be good fortune players, endeavor to reduction the intrinsic clubhouse house edge by keeping a running tally of al...
RS Geometry - Shapes & Solids
Geometry is an extension of science concerned with issues of shape, size, relative position of figures, and the lands of space. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a geometer. Geometry emerged autonomously in various early societies as a collection of reasonable learning concerning lengths, territories, and volumes, with components of a formal numerical science rising in t...
Geometry is an extension of science concerned with issues of shape, size, relative position of figures, and the lands of space. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a geometer. Geometry emerged autonomously in various early societies as a collection of reasonable learning concerning lengths, territories, and volumes, with components of a formal numerical science rising in t...
Probability of Life
Likeliness is a measure of the anticipation that an occasion will happen or a proclamation is correct. Probabilities are given a quality between 0 (should not happen) and 1 (will occur). The higher the prospect of an occasion, the more certain we are that the occasion will happen. The thought has been given a proverbial scientific induction in expectation hypothesis, which is utilized broadly ...
Likeliness is a measure of the anticipation that an occasion will happen or a proclamation is correct. Probabilities are given a quality between 0 (should not happen) and 1 (will occur). The higher the prospect of an occasion, the more certain we are that the occasion will happen. The thought has been given a proverbial scientific induction in expectation hypothesis, which is utilized broadly ...
International System of Units Prefixes
The Universal Framework of Units (condensed SI from French: Système worldwide d'unités) is the advanced manifestation of the metric framework. It contains a framework of units of estimation devised around seven base units and the advantage of the number ten. The SI was made in 1960, dependent upon the metre-kilogram-second framework, as opposed to the centimetre-gram-second framework, which, in tu...
The Universal Framework of Units (condensed SI from French: Système worldwide d'unités) is the advanced manifestation of the metric framework. It contains a framework of units of estimation devised around seven base units and the advantage of the number ten. The SI was made in 1960, dependent upon the metre-kilogram-second framework, as opposed to the centimetre-gram-second framework, which, in tu...
SC Calculus I (1)
Calculus is a limb of maths centred on points of confinement, methods, derivatives, integrals, and unbounded sequence. This subject constitutes a major part of up to date arithmetic training. It has two major limbs, differential maths and necessary analytic, which are identified by the basic theorem of analytic. Maths is the investigation of change, in the same way that geometry is the investigati...
Calculus is a limb of maths centred on points of confinement, methods, derivatives, integrals, and unbounded sequence. This subject constitutes a major part of up to date arithmetic training. It has two major limbs, differential maths and necessary analytic, which are identified by the basic theorem of analytic. Maths is the investigation of change, in the same way that geometry is the investigati...
RS Algebra Properties
Arithmetical geometry is a limb of math, traditionally considering lands of the sets of zeros of polynomial mathematical statements. Advanced logarithmic geometry is dependent upon additional conceptual procedures of unique polynomial math, in particular commutative polynomial math, with the dialect and the situations of geometry.
Arithmetical geometry is a limb of math, traditionally considering lands of the sets of zeros of polynomial mathematical statements. Advanced logarithmic geometry is dependent upon additional conceptual procedures of unique polynomial math, in particular commutative polynomial math, with the dialect and the situations of geometry.
SC Calculus II (1)
Numerous mathematicians, incorporating Maclaurin, tried to confirm the soundness of utilizing infinitesimals, yet it could not be until 150 years later when, because of the work of Cauchy and Weierstrass, an implies was at long last recognized to evade simple "thoughts" of limitlessly modest amounts. The foundations of differential and essential calculus had been laid. In Cauchy's composing, we di...
Numerous mathematicians, incorporating Maclaurin, tried to confirm the soundness of utilizing infinitesimals, yet it could not be until 150 years later when, because of the work of Cauchy and Weierstrass, an implies was at long last recognized to evade simple "thoughts" of limitlessly modest amounts. The foundations of differential and essential calculus had been laid. In Cauchy's composing, we di...
SC Calculus Reference (1)
Differential calculus is the study of the definition, lands, and requisitions of the derivative of a method. The procedure of discovering the derivative is called differentiation. Given a role and a focus in the realm, the derivative at that indicate is a way of encoding the modest-scale conduct of the role close to that indicate. By discovering the derivative of a capacity at each focus in its sp...
Differential calculus is the study of the definition, lands, and requisitions of the derivative of a method. The procedure of discovering the derivative is called differentiation. Given a role and a focus in the realm, the derivative at that indicate is a way of encoding the modest-scale conduct of the role close to that indicate. By discovering the derivative of a capacity at each focus in its sp...
SC Calculus Reference (2)
Integral calculus is the investigation of the definitions, lands, and provisions of two identified ideas, the uncertain essential and the unambiguous vital. The procedure of discovering the quality of an indispensable is called incorporation. In specialized dialect, basic analytics studies two identified direct specialists.
Integral calculus is the investigation of the definitions, lands, and provisions of two identified ideas, the uncertain essential and the unambiguous vital. The procedure of discovering the quality of an indispensable is called incorporation. In specialized dialect, basic analytics studies two identified direct specialists.
QS Statistics (4)
Some acknowledge statistics to be a scientific collection of science relating to the accumulation, examination, elucidation or clarification, and presentation of data, while others recognize it a limb of mathematics concerned with gathering and deciphering information. Due to its experimental roots and its center on requisitions, statistics is typically acknowledged to be a different numerical sci...
Some acknowledge statistics to be a scientific collection of science relating to the accumulation, examination, elucidation or clarification, and presentation of data, while others recognize it a limb of mathematics concerned with gathering and deciphering information. Due to its experimental roots and its center on requisitions, statistics is typically acknowledged to be a different numerical sci...
QS Statistics (3)
The saying statistics, when pointing to the experimental train, is solitary in "Statistics is an art." This might as well not be confounded with the expression statistic, pointing to an amount (for example mean or average) figured from a set of data, whose plural is statistics ("this statistic appears wrong" or "these statistics are misdirecting").
The saying statistics, when pointing to the experimental train, is solitary in "Statistics is an art." This might as well not be confounded with the expression statistic, pointing to an amount (for example mean or average) figured from a set of data, whose plural is statistics ("this statistic appears wrong" or "these statistics are misdirecting").
SC Algebra I (4)
Unique algebra based maths was upgraded in the 19th century, deriving from the premium in handling examinations, from the get go fixating on what is now called Galois speculation, and on constructibility issues. The "present day polynomial maths" has significant nineteenth-century creates in the work, for example, of Richard Dedekind and Leopold Kronecker and critical interconnections with diverse...
Unique algebra based maths was upgraded in the 19th century, deriving from the premium in handling examinations, from the get go fixating on what is now called Galois speculation, and on constructibility issues. The "present day polynomial maths" has significant nineteenth-century creates in the work, for example, of Richard Dedekind and Leopold Kronecker and critical interconnections with diverse...
SC Calculus I (2)
Calculus has generally been called "the math of infinitesimals", or "minute analytics". For the most part, analytics (plural calculi) points to any system or framework of count guided by the symbolic control of declarations. Certain samples of different well-known calculi are propositional analytics, variational math, lambda math, pi analytics, and unite math.
Calculus has generally been called "the math of infinitesimals", or "minute analytics". For the most part, analytics (plural calculi) points to any system or framework of count guided by the symbolic control of declarations. Certain samples of different well-known calculi are propositional analytics, variational math, lambda math, pi analytics, and unite math.
Mathematical Relationships
In arithmetic, a twofold connection on a set An is an accumulation of requested matches of components of A. In different expressions, its a subset of the Cartesian feature A2 = A × A. Ordinarily, a binary connection between two sets An and B is a subset of A × B. The terms dyadic connection and 2-place connection are synonyms for double relations. An illustration is the "partitions" connection...
In arithmetic, a twofold connection on a set An is an accumulation of requested matches of components of A. In different expressions, its a subset of the Cartesian feature A2 = A × A. Ordinarily, a binary connection between two sets An and B is a subset of A × B. The terms dyadic connection and 2-place connection are synonyms for double relations. An illustration is the "partitions" connection...

 Upload your infographic here and contribute to our community.
Upload your infographic here and contribute to our community. 
Leave a Reply